Specific Heat Capacity Definition
The definition of C n is often related to a certain application or battery testing standard. The Scottish scientist Joseph Black in the 18th century noticed that equal masses of.
Does Atmospheric Pressure Affect Specific Heat Capacity Quora
A change in internal energy can be expressed as.

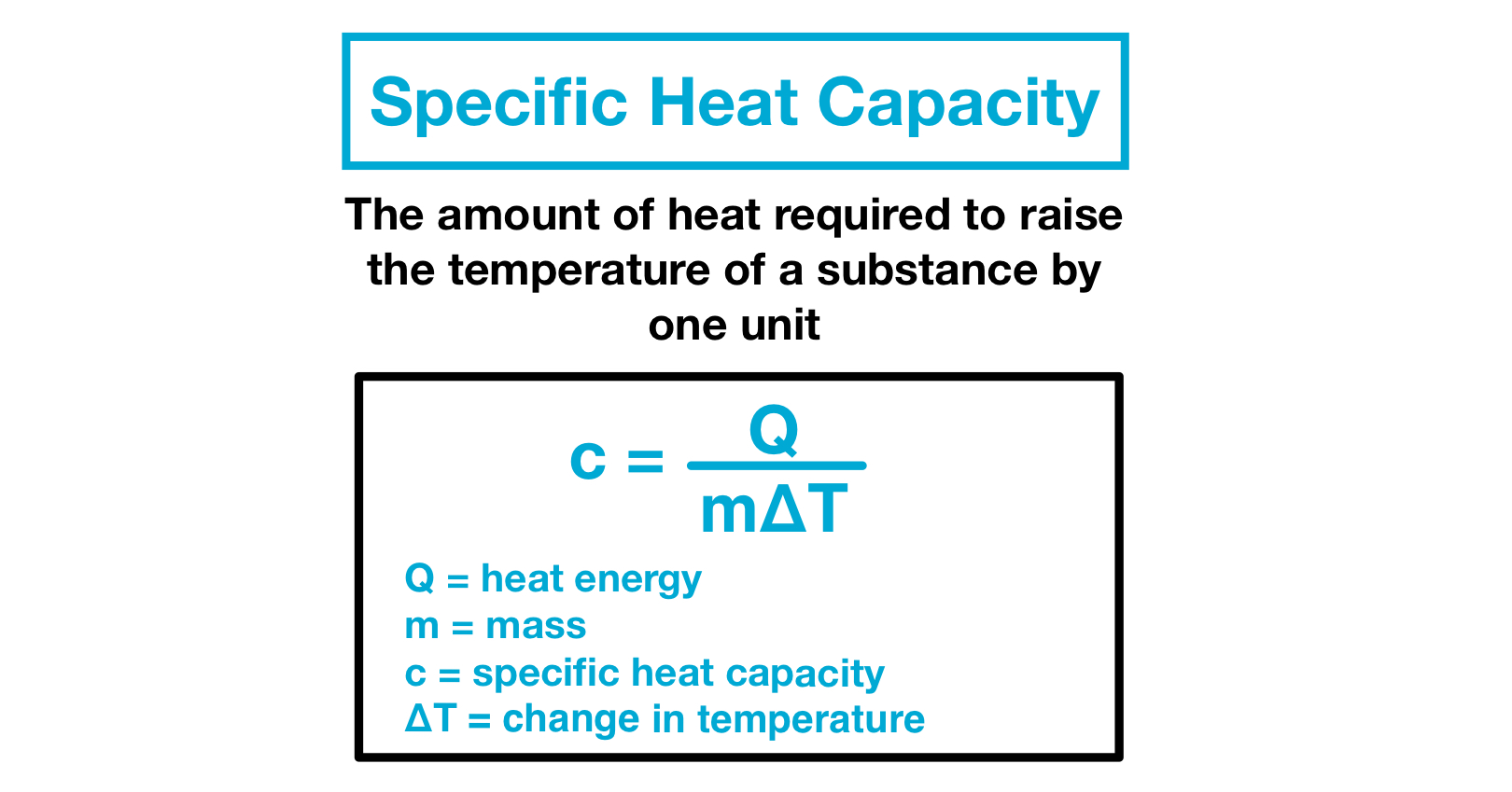
. C p specific heat capacity. The below-mentioned formula can be used to calculate specific heat capacity values. Specific heat can be defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celsius.
Heat capacity ratio of heat absorbed by a material to the temperature change. Where Q is the heat capacity in Joules. The specific enthalpy h of a substance is its enthalpy per unit mass.
Du change in internal energy kJkg. For an ideal gas the internal energy - u - is a function of temperature. Therefore specific heat capacity c Qm Delta T.
Experiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated Temperatures 2011. 845-870 C 1550-1600 F rate of cooling. Formula for Heat Capacity.
The heat capacity in calories per gram is called specific heat. The value of the constant is different for different materials and depends on the process. Commonly quoted and tabulated in the literature are the.
The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin JK. The units to express specific heat capacity are calK cal JK and J. What is Specific Heat.
The heat Capacity formula is expressed as the product of mass specific heat and change in the temperature which is mathematically given as. The time to maintain the temperature ranges from 1 hour for light steel to 4 hours for heavy steel and high. Thus the correct option is A.
Or nameplate capacity denoted as C n. The enthalpy can be made into an intensive or specific variable by dividing by the mass. It equals to the total enthalpy H divided by the total mass m.
The method of mixture is used almost universally by scientists as a quick easy and semi-accurate specific heat test for a solid sample but what makes this method extra special is the fact that its so simple that high school students around the world perform it as a hands-on example of how the specific heat capacities of materials are a part of the world around us. DT change in temperature K. Methanol with molecular formula CH3OH has a molar heat capacity C p of 811 Jmol K.
If youre given the amount of energy used the mass and initial temperature heres how to calculate the final temperature of a reaction. The specific heat capacity can be calculated from the molar heat capacity and vise versa. Goldratt and further developed Eli Schragenheim constraints can only be located in a few specific places.
Specific heat the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one Celsius degree. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of.
The expression for specific heat has been. Q n C T. Specific heat describes the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a kilogram of a substance by 1 o C or 1 KIn some fields the amount of heat required to raise temperature by 1 gram is also often considered.
If we are dealing with a gas it is most convenient to use forms of the thermodynamics equations based on the enthalpy of. For example De Beers controlled 90 of the global diamond market. Specific heat c v varies with temperature but within moderate temperature changes the.
It also significantly depends on the nature size and composition of a substance in a system. For example the nominal capacity of starting lighting and ignition lead-acid battery typically coincides with the 20-h-rated capacity C 20h. A specific latent heat L expresses the amount of energy in the form of heat Q required to completely effect a phase change of a unit of mass m usually 1 kg of a substance as an intensive property.
Definition of molar Heat Capacity C The total amount of energy in the form of heat needed to increase the temperature of 1 mole of any substance by 1 unit is called the molar heat capacity C of that substance. For example the specific heat of water is 1 calorie or 4186 joules per gram per Celsius degree. The heat capacity of a defined object is usually expressed in joules or calories and temperature in Kelvin or Celsius.
The units of specific heat are usually calories or joules per gram per Celsius degree. It is usually expressed as calories per degree in terms of the actual amount of material being considered most commonly a mole the molecular weight in grams. Calorie or Joule g specific.
C p molar heat capacity. Heat capacity is not a state variable. The nominal capacity can be used to.
Du c v dT 1 where. Is where a company captures the bulk of the market and runs out of further space to grow. Specific Heat Capacity c Specific heat capacity of any substance is defined as the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by 1 degree.
If a substance having a mass is given an energy and this results in a gain in temperature the specific heat is given by. Sulfur has a theoretical specific capacity and specific energy of 1672. The specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat J absorbed per unit mass kg of the material when its temperature increases 1 K or 1 C and its units are Jkg K or Jkg C.
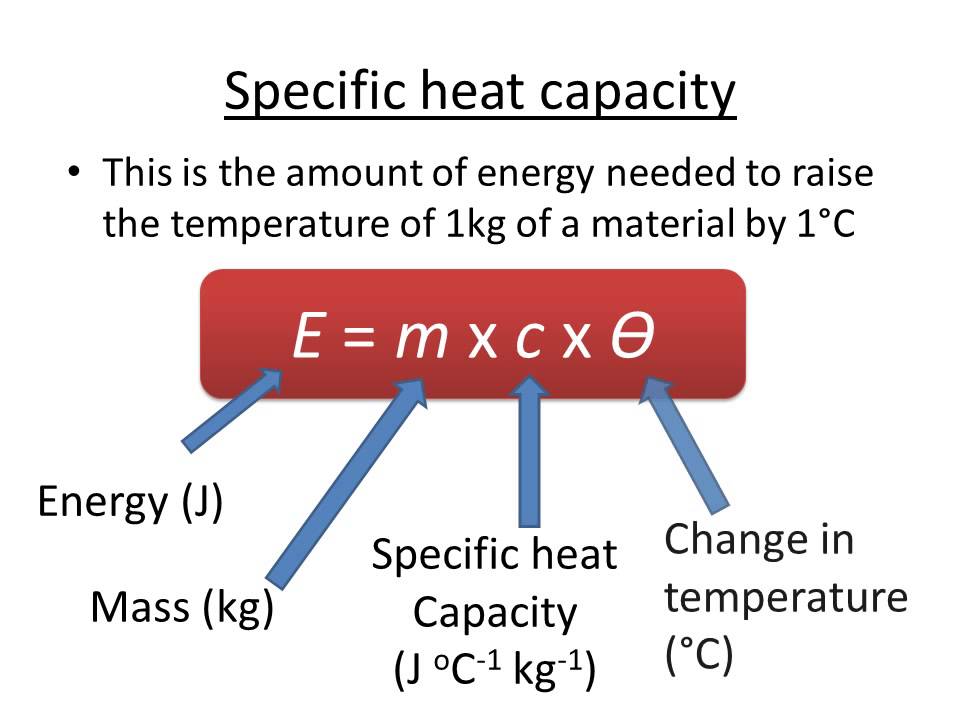
Definition of Specific heat capacity revealed that it is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kilogram of any substance by 1 kelvin. Heat capacity is an extensive propertyThe corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity found by dividing the heat capacity of an object. C p c p.
C v specific heat for gas in a constant volume process kJkgK. Going by the narrow definition of constraint pioneered by Dr. Heat mass specific heat capacity change in temperature.
C p C p M and. The heat capacity is a constant that tells how much heat is added per unit temperature rise. Where q is the heat supplied or needed to bring about a.
Intensive properties are material characteristics and are not dependent on the size or extent of the sample. Specific Heat Capacity Unit. The definition of the calorie is based on the specific heat of water defined.
Hence its derived SI unit is J kg1 K1. Q mc Delta T. The upper limit of the range should be applied to the large section while the lower limit for the smaller section.
Engineers use the specific enthalpy in thermodynamic analysis more than the enthalpy itself. M molar weight of the actual substance gmol. A2 steel annealing heat treat temperature.
A specific heat capacity calculator is functioned to deliver the outcomes along with standardized units. 22 Ch 40 Fh to 705 C 1300 F Brinell hardness is 201-229 HB.
Heat Capacity Of Water Overview Importance Expii

Specific Heat Definition Facts Britannica
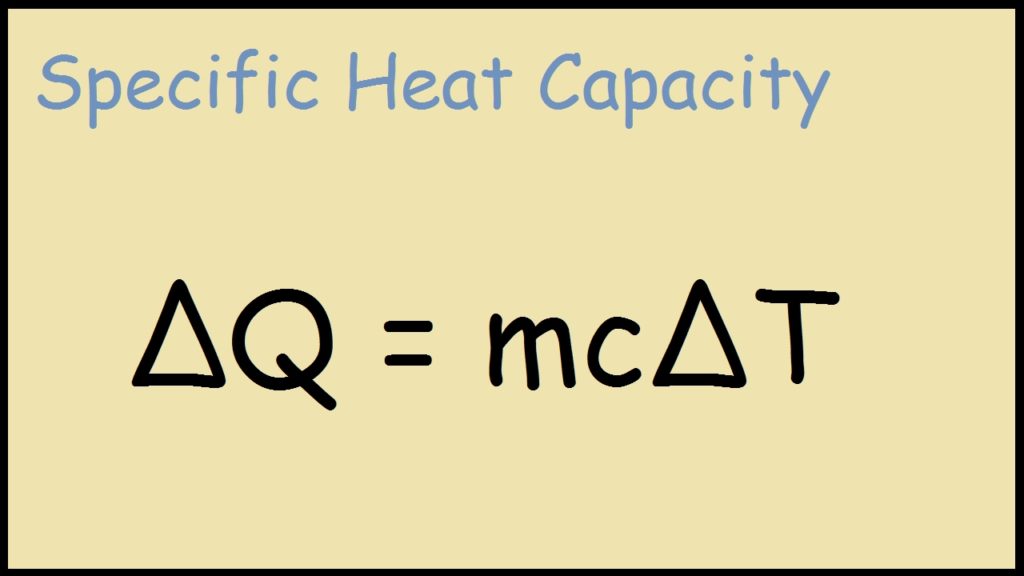
No comments for "Specific Heat Capacity Definition"
Post a Comment